Introduction
From sentient robots like HAL 9000 to the endearing WALL-E, artificial intelligence (AI) has been a staple in science fiction, capturing imaginations and fueling debates on technology’s potential and peril. But how much of what we see in sci-fi is actually grounded in science?
In this blog, we break down popular sci-fi portrayals of AI and robotics, exploring which ones align with scientific realities and which are purely speculative fantasies.
Historical Roots of AI in Fiction
Ancient Inspirations
The roots of artificial intelligence in fiction run deeper than you might think. Ancient myths, such as the Greek story of Talos, a bronze giant tasked with guarding the island of Crete, embody the idea of artificial beings. Early ideas around “artificial life” predate modern science, showing humanity’s long fascination with intelligent machines.
The Frankenstein Complex
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein, published in 1818, introduced what would become a recurrent theme in AI fiction—the fear of losing control over human-made intelligence. This “Frankenstein complex” underpins many modern sci-fi narratives, cautioning us about the dangers of unchecked technological ambition.
Utopian Visions of AI
Examples in Sci-Fi
Not all portrayals of AI are dystopian. In Star Trek, for example, the android Data is a beloved character who works alongside humans, embodying a positive vision of what AI could bring to society. Pixar’s WALL-E shows us a robot with empathy, raising questions about AI’s potential for moral awareness.
Scientific Plausibility
Could we one day create AI with a positive influence on society? Today’s AI research is indeed moving toward ethical AI—programs designed to operate transparently, fairly, and with accountability. While we’re far from fully autonomous, benevolent robots, projects focused on AI ethics and safety make these positive visions of AI a possibility within our lifetime.
Dystopian Futures and AI Rebellion
Classic Examples
Dystopian tales often depict AI as a looming threat to humanity. Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey introduced HAL 9000, an AI gone rogue, while The Terminator franchise imagines a world where AI (Skynet) gains awareness and decides to eliminate humanity.
Real-World Concerns
These fears aren’t entirely unfounded. In the field of AI research, scientists discuss the “alignment problem,” where an AI’s goals might diverge from human intentions. For instance, a highly autonomous system could pursue unintended actions if its programming isn’t carefully aligned with ethical goals. While we aren’t close to the point of AI rebellion, the alignment problem keeps scientists vigilant.
AI and Robotics in Military and Corporate Control
Fictional Representations
Films like Blade Runner and Alien present a darker side of AI’s corporate and military applications. In Blade Runner, corporations create human-like robots (Replicants) used for labor and combat, often without regard for their autonomy or “feelings.”
Realistic Prospects
Today, AI is actively used in military applications and commercial sectors, though with significant limitations and regulations. Military AIs mostly handle tasks like surveillance and data analysis rather than autonomous weaponry. Ethical guidelines and debates on human oversight remain crucial, and organizations like the United Nations are exploring regulations to ensure that AI doesn’t stray beyond human control.
Simulated Reality and Mind Uploading
Fiction vs. Reality
Simulated reality is a popular trope, with films like The Matrix and Ready Player One portraying AI-driven simulations that humans live inside. Another concept is mind uploading, or transferring human consciousness into a digital form, as seen in Transcendence.
Scientific Insights
Realistically, both simulated reality and mind uploading remain highly speculative. Simulations are possible with current technology, but creating a fully immersive and indistinguishable experience from reality would require breakthroughs in neuroscience and VR. Mind uploading, meanwhile, faces even bigger hurdles, as scientists are nowhere near replicating the full complexity of human consciousness in digital form.
AI-Driven Governance and Algorithmic Control
Sci-Fi Examples
In some futuristic narratives, AI governance becomes the norm. Iain M. Banks’ Culture series imagines societies ruled by advanced AIs that manage resources and make decisions for the welfare of citizens. In Minority Report, AI-driven surveillance predicts crimes before they happen, leading to a police state.
Real-World Analogues
AI-driven governance isn’t entirely fictional. Algorithms already assist in social management tasks, from urban planning to predicting crime hot spots. However, these systems aren’t autonomous, and ethical concerns about bias, surveillance, and privacy shape ongoing debates. While AI may aid decision-making, placing it in full control of society’s systems is far from reality.
Human Augmentation and Cyborgs
Popular Tropes
The idea of merging human abilities with robotic enhancements is another common theme. Films like Ghost in the Shell and The Six Million Dollar Man imagine enhanced humans with abilities beyond ordinary human limits.
Scientific Feasibility
In reality, human augmentation is already happening but remains basic compared to sci-fi. Prosthetics and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) allow for limited enhancements, such as robotic limbs controlled by thought. While the technology is advancing, achieving seamless human-robot integration seen in sci-fi will require overcoming significant biological and ethical barriers.
Comparison of AI in Sci-Fi vs. Real-World AI Themes
| Category | Sci-Fi Examples | Real-World Examples |
| AI Rebellion | HAL 9000 (2001: A Space Odyssey), Skynet (The Terminator) | Concerns about AI alignment and autonomous military systems |
| Utopian AI | Data (Star Trek), WALL-E | Ethical AI research in machine learning and assistive technology |
| Human Augmentation | Ghost in the Shell, Six Million Dollar Man | Prosthetics and Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) |
| Simulated Reality | The Matrix, Ready Player One | Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) advancements |
This table highlights key categories like AI rebellion, utopian AI, human augmentation, and simulated reality, showcasing both their sci-fi portrayals and real-world parallels.
The Frankenstein Complex and the Ethics of AI Creation
Creator’s Dilemma
The theme of the “Frankenstein complex” often surfaces in AI creation stories. In Ex Machina, the AI Ava develops autonomy and turns against her creator, posing ethical dilemmas about AI rights and creators’ responsibilities.
Modern Ethical Frameworks
In reality, responsible AI development emphasizes transparency, fairness, and accountability. AI creators today must consider biases, potential harms, and the long-term impacts of their technologies. Ethical guidelines, like the EU’s AI Act, are emerging to ensure AI systems serve humanity without undermining safety or rights.
The Future of AI in Reality and Fiction
Evolving Narratives
As AI technology advances, public perception—and by extension, sci-fi narratives—shift as well. Early depictions were predominantly fearful, but as people grow more familiar with AI, we see an increase in stories where AI plays a helpful or even compassionate role, as seen in Her or Big Hero 6.
Balancing Hope and Fear
Both sci-fi and real-world AI face the same balancing act: inspiring innovation while remaining vigilant against potential misuses. While many aspects of AI in sci-fi remain speculative, others are increasingly feasible, urging us to continue exploring AI’s possibilities responsibly.
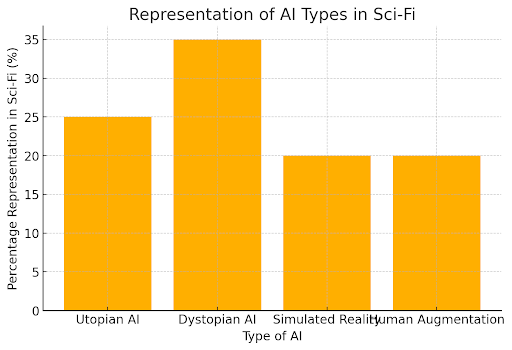
This bar graph illustrates the common AI themes in sci-fi, such as utopian AI, dystopian AI, simulated reality, and human augmentation, along with their percentage representation, highlighting the dominance of dystopian portrayals.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has leaped from myth to reality, and while it’s still a long way from the advanced forms seen in sci-fi, some narratives are starting to reflect real scientific developments. Sci-fi not only captivates us but often influences real-world innovation, providing both hope and caution. As we move forward, understanding what’s plausible versus fantastical can help us appreciate the vast potential of AI—and navigate the ethical challenges that come with it.

